Atoms are tiny particles of matter which make up everything in the universe. Everything you see is made up of atoms.
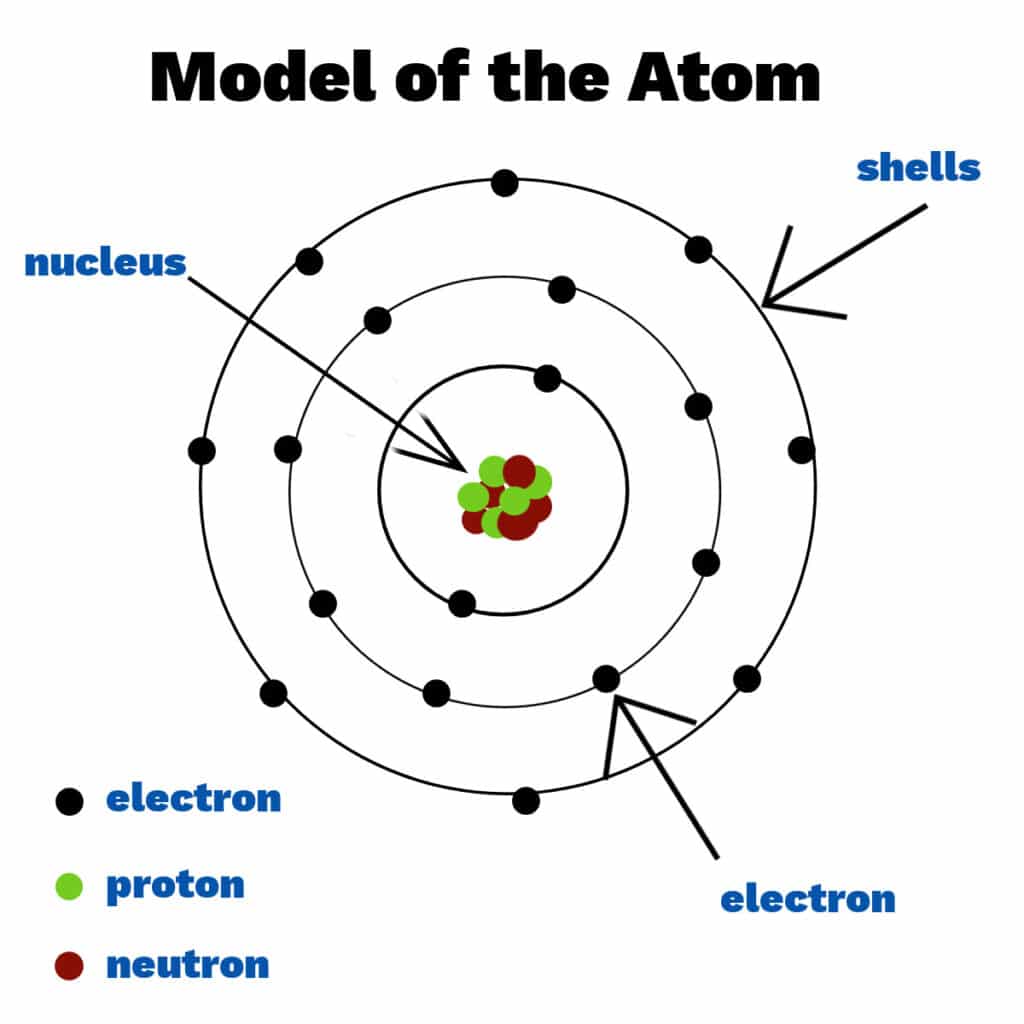
Scientists spent many years trying to understand the structure of the atom, with several models and theories being disproved or improved upon along the way. Today we know that atoms consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by shells ( energy levels ) of electrons. Electrons, protons and neutrons are known as subatomic particles. Each shell holds a fixed number of electrons.
Atoms from different elements have different numbers of electrons, protons and neutrons.
Theory of Atomic Structure
John Dalton
John Dalton is often known as the father of atomic theory. He proposed a theory of the atom in 1803.
John Dalton believed that:
All matter is made of atoms
Atoms were solid spheres – later disproved
Atoms within an element are the same. Atoms from different elements are not.
Atoms couldn’t be further broken down – later disproved
Atoms are rearranged during a chemical reaction but are not lost. This is the Law of Conservation of Mass.
JJ Thomson
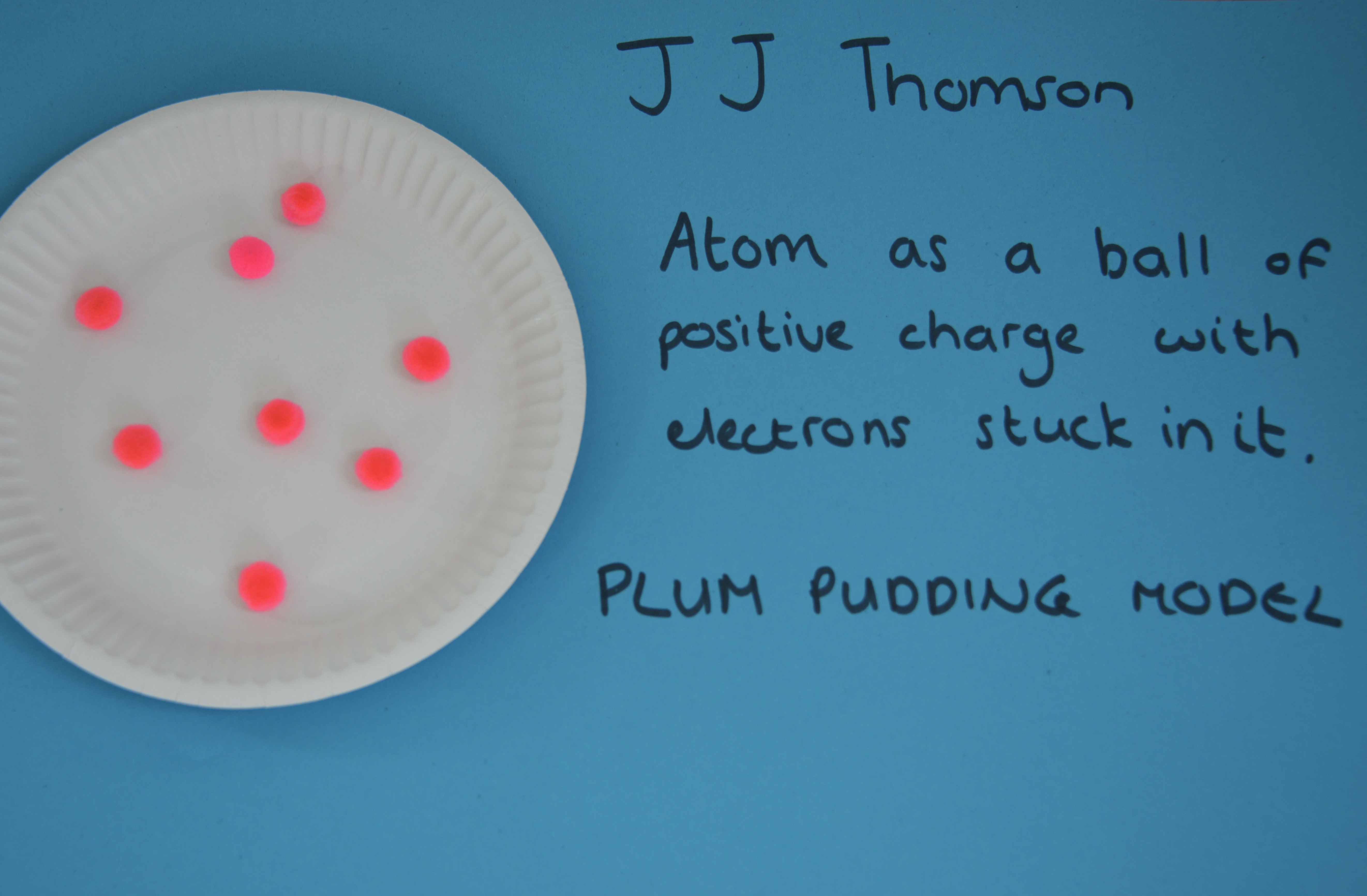
In 1897, JJ Thomson proposed that atoms were not solid spheres. His research showed that atoms must contain negatively charged particles ( electrons ). This theory is known as the plum pudding model.
Ernest Rutherford
In 1909, Ernest Rutherford and two of his students conducted the now-infamous gold foil experiment. They fired positively charged alpha particles at a very thin sheet of gold. If the plum pudding model were correct, the particles would either pass through the sheet of gold or be very slightly deflected as the charge was thought to be spread through the atom. Gold was chosen as it can be made very thin.
While most particles did pass through, some were deflected more than Rutherford expected, and some were deflected backwards, showing that the plum pudding model could not be correct. Rutherford developed a theory where the atom had a tiny positively charged nucleus in the centre with a cloud of negative electrons surrounding it.
Alpha particles fired towards the gold foil were either deflected backwards if they were close to the nucleus or passed through the empty space of the atom.

Niels Bohr
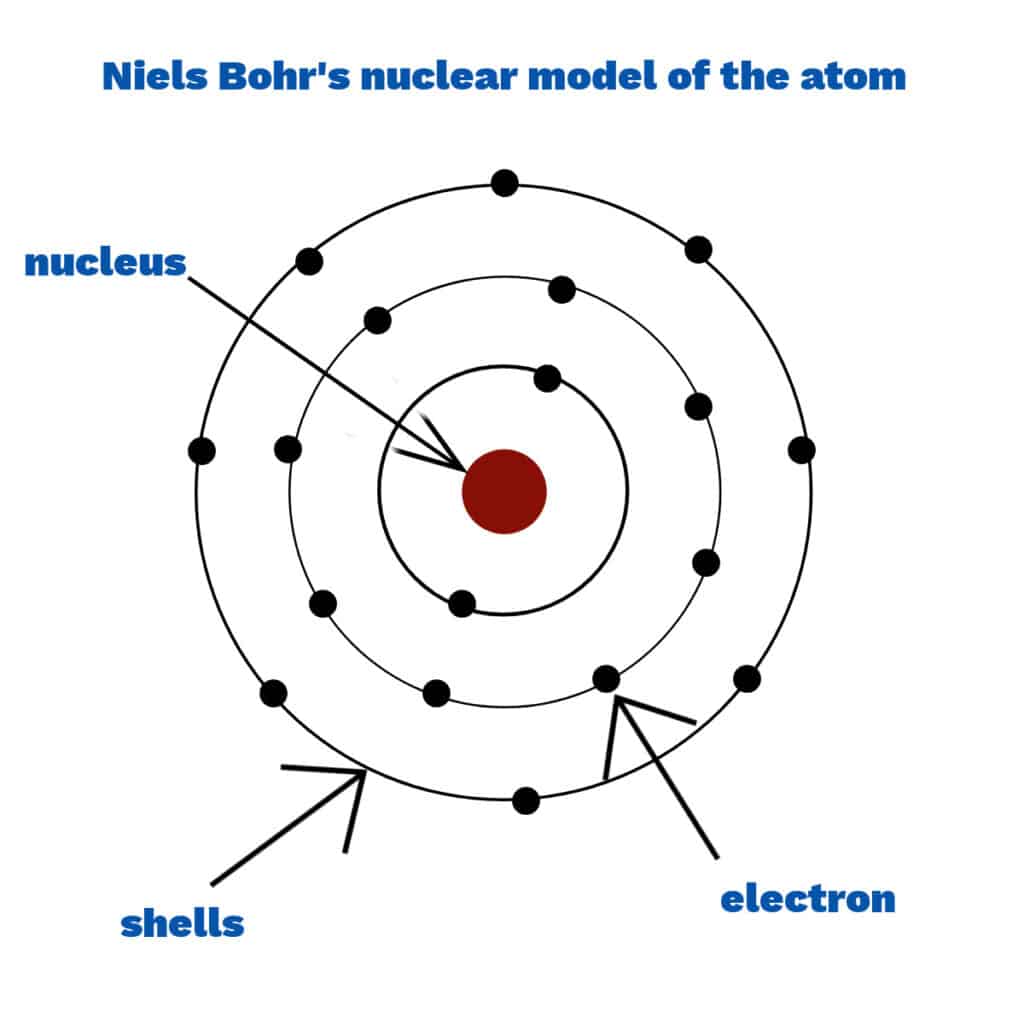
Niels Bohr developed a model of the atom with electrons arranged in fixed shells around the nucleus instead of in a cloud. Scientists thought that electrons in a cloud would be attracted to the nucleus, making the atom collapse.

James Chadwick
James Chadwick conducted experiments demonstrating that atoms have neutral particles ( neutrons ) in their nucleus. James Chadwick’s model is very close to the modern-day nuclear model of the atom!

Learn more about the history of the atom
Learn more about Ernest Rutherford, who was awarded a Nobel Prize for his work on atomic structure.
Discover how Ernest Schrödinger extended the model proposed by Bohr.

Last Updated on May 19, 2023 by Emma Vanstone
